Crux Alliance will co-host two events at New York Climate Week!
Charging Ahead: Global Strategies for Bus Electrification
We know electric cars alone won’t save the climate. To limit global heating, cities must get drivers out of cars and into reliable, all-electric bus systems. By doing so, cities can lower housing and transport costs for residents, cut pollution, enhance livability, and promote equity.
This Climate Week event will bring together policymakers, sustainable transportation experts, and climate funders to share how they collaborate to overcome political, financial, and technological challenges, and to illuminate key lessons learned for other global cities charting the path to electric transport for all.

Global Perspectives: Energy Justice and the Future of Climate
As we push for a clean energy transition that benefits all communities, it’s vital that we share insights across regions and sectors to accelerate progress. This special Climate Week event brings together experts from diverse backgrounds to dive deep into issues like energy access, affordability, and reducing burdens on local communities. With local communities on the front lines of climate change, global dialogue on equity is more important than ever. Space is limited, so please contact us to attend.

APPLIANCES

New toolkit helps governments prioritize appliance efficiency in Paris climate commitments
CLASP recently launched its Net Zero Appliances NDC Toolkit to help over 160 countries slash emissions by incorporating appliance efficiency targets into their national commitments to the Paris Agreement, known as nationally determined contributions (NDCs). With the deadline for countries to submit their revised NDCs approaching in 2025, the toolkit provides essential resources at a pivotal moment. This update period is crucial, as the next mandatory revision doesn’t occur until 2030. Appliance efficiency is a vital, yet often overlooked, climate solution. To date, only 47 percent of NDCs mention appliances, while only 25 percent specify the policies needed to reduce appliances’ contribution to climate change. The toolkit contains recommendations and resources to help governments assess, design, and draft net-zero-aligned targets for appliances and equipment.

URBAN MOBILITY

Drawing inspiration from Jinan’s trolley buses to scale solutions in China
The electrification of bus systems has never been more urgent for improving public transport efficiency and reducing related emissions. This is especially true in a rapidly urbanizing nation like China, where many cities are turning to electric trolley buses as a zero-emission transit solution. In July and August, the Institute for Transportation and Development Policy (ITDP) China team conducted an in-depth field study and tour of the city of Jinan’s trolley system developed by the Jinan Public Transport Group. ITDP’s trip helped gather important best practices and lessons for the development of a guidebook for the Asian Development Bank (ADB) that will be used as a model for other Chinese cities looking to implement similar bus projects. Jinan’s system was financed by the ADB and currently includes over 75 kilometers of bus priority lanes served by a fleet of 350-plus electric buses, which are expected to reduce CO2 emissions by nearly 250,000 tons yearly.

VEHICLES AND FUEL

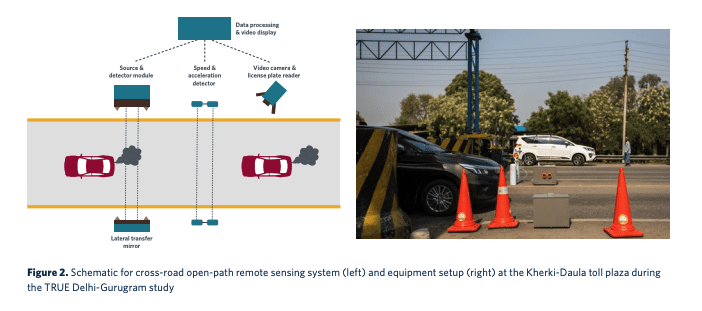
Study finds Delhi’s motor vehicles emit far more in real-world operations as compared to lab setting
Delhi and the nearby city of Gurugram have suffered the debilitating impacts of poor air quality for decades, and the transport sector has been a major contributor. The Real Urban Emissions (TRUE) Initiative, with support from the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) and FIA Foundation, worked in collaboration with authorities in Delhi and Gurugram to test emissions of on-road vehicles with non-intrusive remote sensing technology. The final report, featuring technical analysis by the ICCT, offers insights into real-world tailpipe emissions from vehicles in Delhi and Gurugram and supports evidence-based policymaking to reduce pollution. Key findings include:
- Vehicles meeting the latest Bharat Stage VI emissions standard showed up to 95 percent lower NOx emissions for buses.
- However, many vehicles still exceed emissions limits in real-world driving, with some vehicles emitting up to five times more NOx than expected.
- Compressed natural gas vehicles were up to 14 times higher than their lab limits.
These findings emphasize the need to move beyond lab results and focus on reducing real-world vehicle emissions to effectively tackle air pollution in Delhi and Gurugram.
BUILDINGS

Supporting implementation of the Buildings Breakthrough Agenda
The Global Buildings Performance Network (GBPN) is supporting signatories to the Buildings Breakthrough and Declaration de Chaillot to strengthen buildings sector actions in revised NDCs, and to implement common green building standards in Southeast Asia through ASEAN and Green Global Growth Institute Programs. As a supporting initiative of the Buildings Breakthrough, GBPN is supporting development of Kenya’s National Decarbonization Plan and Climate Change, Green and Resilient Buildings Regulations and the updating of its NDC at the invitation of the Ministry of Public Works and Housing. As a first phase, GBPN convened a workshop in August on decarbonizing the built environment in Kenya in collaboration with key stakeholders. “We’ve partnered with the Ministry of Environment and other players in the industry to ensure that we have a common agenda. I want to thank GBPN for partnering with us and taking the lead in bringing other players in the industry to this very important road map,” said Joel Arumonyang, Principal Secretary of the State Department of Public Works.

POWER

New rules will increase clean alternatives to coal in China
In response to power crises in 2021, China shifted approaches to coal-fired power plants that relaxed coal investment procedures and, by the end of 2023, led to a coal power-only capacity payment policy (capacity payments pay providers for the power they can provide). RAP has consistently championed integrating clean and efficient demand-side resources (like rooftop solar, batteries, and demand-response) to meet growing electricity needs, particularly promoting a diverse set of clean energy resources for capacity payment eligibility. RAP’s analysis and recommendations were disseminated through multiple publications in high-impact platforms read by key stakeholders. And this summer Jiangsu Province and the city of Chongqing introduced new policies that include capacity payments for certain demand-side resources such as virtual power plants. This policy shift is crucial for generating new revenue for clean energy resources that also can outperform coal plants. This policy could reduce future investments in coal plants and emissions from existing facilities.

GreenCape helps drive approval of landmark South African Renewable Energy Masterplan
In June, the South African Renewable Energy Masterplan (SAREM) was approved for implementation by the Department of Minerals and Energy’s executive committee, paving the way for signature by all parties. SAREM is a national renewable energy industrialization plan developed as a social compact between government, business, and labor unions. It sets targets for renewable energy industrial growth and job creation, based on a minimum renewable energy rollout of 3 GW per year, increasing to 5 GW per year by 2030. GreenCape, a member of the International Network of Energy Transition Think Tanks hosted by Agora Energiewende, has been pivotal in SAREM’s development since 2020, managing the project, coordinating research and consultations, and drafting the plan. Despite the African National Congress losing its majority in June, the new Government of National Unity is expected to favor a broad political endorsement of SAREM, with its emphasis on reform and merit-based public service increasing the likelihood of political support. SAREM’s ratification marks a significant step toward a more sustainable and inclusive economy, showcasing how collaboration between government and various groups can steer change.

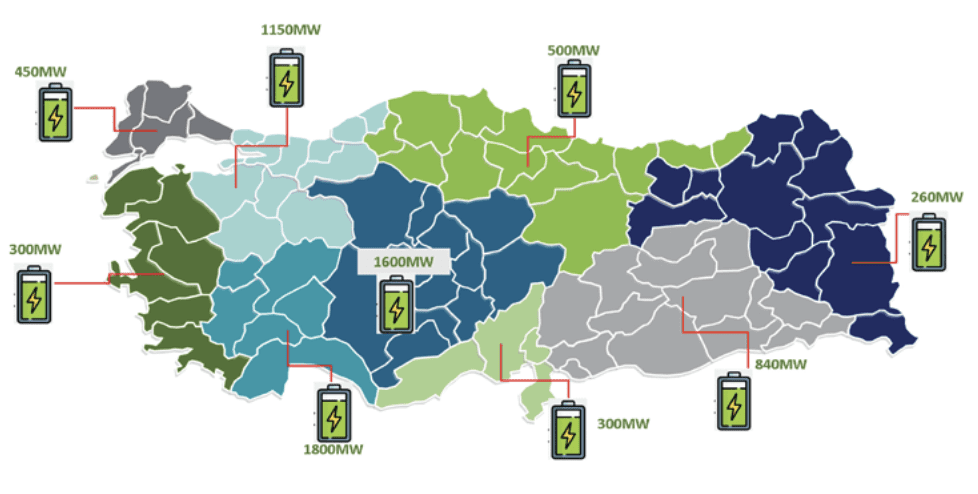
SHURA report outlines pathways to grow battery energy storage systems in Türkiye
As Türkiye accelerates efforts to expand renewable energy, it is developing key regulations to support this transition. By June 2024, 32 gigawatts of pre-licenses for battery storage systems integrated with renewable power plants had been issued, in accordance with current regulations. To support upcoming secondary legislation, SHURA Energy Transition Center, a member of the International Network of Energy Transition Think Tanks hosted by Agora Energiewende, published the Battery Energy Storage Options for Türkiye report in August. It analyzes how battery storage can improve power system flexibility by mapping battery technologies, identifying key services that will benefit most from their adoption, and evaluating transmission grid impacts. The report finds that by 2035, the expected 7.2 gigawatts per 28.8 gigawatt hours of battery capacity could reduce renewable curtailments (when excess renewable energy is wasted) and natural gas consumption by 6.9 and 11.7 terawatt hours, respectively, decrease natural gas imports by $369 million, and cut carbon emissions by 2.3 million tons. Presented to over 550 stakeholders, these insights offer actionable recommendations to help battery storage integrate more renewables into Türkiye’s grid.
INDUSTRY

Agora Industry research informs Germany’s National Circular Economy Strategy
Research by Agora Industry featured prominently in a draft proposal for Germany’s National Circular Economy Strategy, published in July. The Environment Ministry drew on strategies for a more circular economy developed by Agora and its partners in recent publications. Circular economy strategies such as recycling, material efficiency and substitution, and longer product use can help reduce dependencies on imported raw materials. The necessary strategies could be deployed at scale immediately, given the right regulatory framework. The potential cumulative emissions savings from circular use and decarbonized production of basic materials such as steel, concrete, cement, and chemicals in the buildings, automotive, and packaging sectors in Germany—as proposed in the Agora Industry reports—would amount to 300 million tons of CO2e. This would reduce cumulative emissions by about 25 percent compared to a scenario that focuses only on decarbonizing primary production.
